How To Read An Audiogram Conductive Sensorineural
Audiograms are used to diagnose and monitor hearing loss. An audiogram represents an individuals hearing ability by frequency pitch and intensity volume.

Reading An Audiogram Air Vs Bone Conduction L
In an audiogram you would see bone conduction thresholds indicating a hearing loss and the air conduction thresholds showing an even greater hearing loss.

How to read an audiogram conductive sensorineural. How to read an audiogram conductive sensorineural. Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss and deafnes for students preparing for the USMLE. What is an Audiogram.
Hearing loss can be divided into two categories. The closer all the symbols are to the top of the audiogram graph the better your hearing is. A sensorineural hearing loss.
In conclusion conductive hearing loss is the sound can not reach the inner ear sound loudness is affected surgery or medication is more effective. In the audiogram below hearing thresholds for the right ear are represented by red circles and thresholds for the left ear are represented by the blue X. Audiograms are created by plotting the thresholds at which a patient can hear various frequencies.
Audiogram Note Bone Air Gap In Conductive. Differentiating conductive hearing loss from sensorineural hearing loss requires bone conduction testing. In this case your child may already have a sensorineural hearing loss and then develop a conductive loss due to excessive fluid or wax in the ears.
The pathology is in the outer or middle ears. Tympanometric tracings occur one can The overall results indicate a bilateral mild sloping gradually to a severe sensorineural hearing loss. The next step involved examinIn looking at the audiogram tympanic membrane TM mobil the reader will also note the symbols R right and L left at both 500 and.
In the right ear this person has normal hearing in the lower pitches indicated by a red circle corresponding to 15 dB at 250 Hz and 20 dB at 500 Hz. How to read an Audiogram and How to Understand Your hearing test resultswhat do they mean. When reading your audiogram first look at where all the symbols fall.
There is a difference of at least 10 db between the air and bone conduction thresholds. If not then you have a problem in your inner ear a sensorineural hearing. The results of an audiogram can help direct medical and surgical interventions to improve andor preserve hearing function.
The audiogram shows normal bone conduction thresholds while the air conduction thresholds show a hearing loss greater than 20db remember 0- 20 db is normal range. Understanding the information shown on an. CONDUCTIVE HEARING LOSS DEAFNESSConductive hearing loss invovles.
You have both we call it mixed losses ie conductive sensorineural. An Audiogram is a graph that shows the. Then look to see if the bone conduction is in the normal range above 20dB.
Audiometry relies on techniques similar to the Weber and Rinne tests to.

How To Read An Audiogram Iowa Head And Neck Protocols

Audiometry Screening And Interpretation American Family Physician

Air Conduction Vs Bone Conduction Candidacy Guide For Bone Conduction Systems Med El Professionals Blog
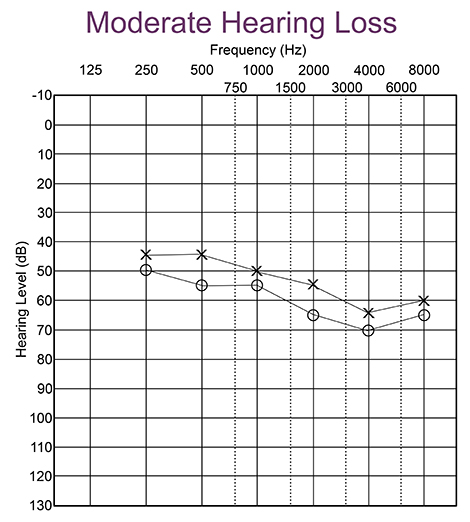
What Is An Audiogram Understanding Hearing Test Results Babyhearing Org

Air Conduction Vs Bone Conduction Candidacy Guide For Bone Conduction Systems Med El Professionals Blog

How To Read An Audiogram Emoyo Technologies
Audiograms Hearing Loss Dhh Education

Air Conduction Vs Bone Conduction Candidacy Guide For Bone Conduction Systems Med El Professionals Blog
Audiograms Hearing Loss Dhh Education
Audiograms Hearing Loss Dhh Education

How To Read An Audiogram Emoyo Technologies

Audiometry Screening And Interpretation American Family Physician

Audiometry Screening And Interpretation American Family Physician
Reading An Audiogram The Effective How To Guide
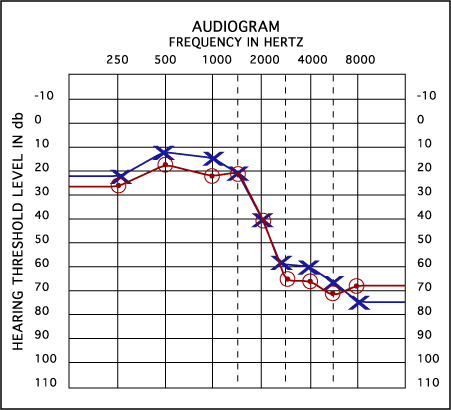
Interpret Your Audiogram National Dizzy Balance Center
Clinical Junior Com How To Read Audiogram And Tympanogram

How To Interpret An Audiogram 2 2013 By Dr Khaled A Abulfadle Youtube
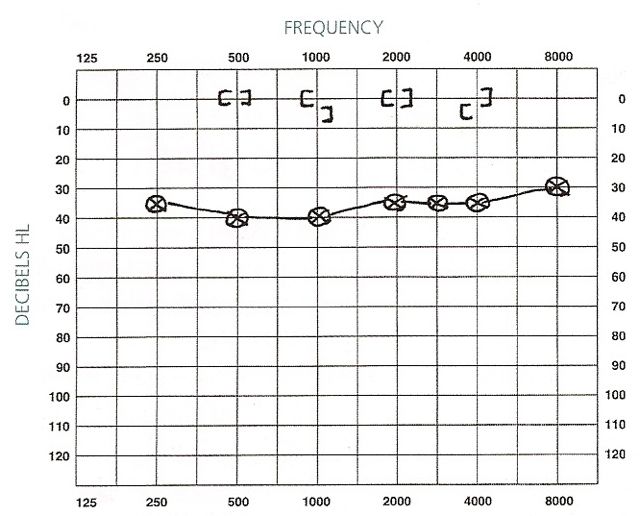
Post a Comment for "How To Read An Audiogram Conductive Sensorineural"